In the present day, where sustainability and protection of the environment are increasingly paramount, recycling plays an important role to reduce waste and conserve natural resources. But have you ever wondered how scrap moves from your home, office, or factory to a recycling plant?
Let’s have a detailed look at the scrap recycling process- step by step.
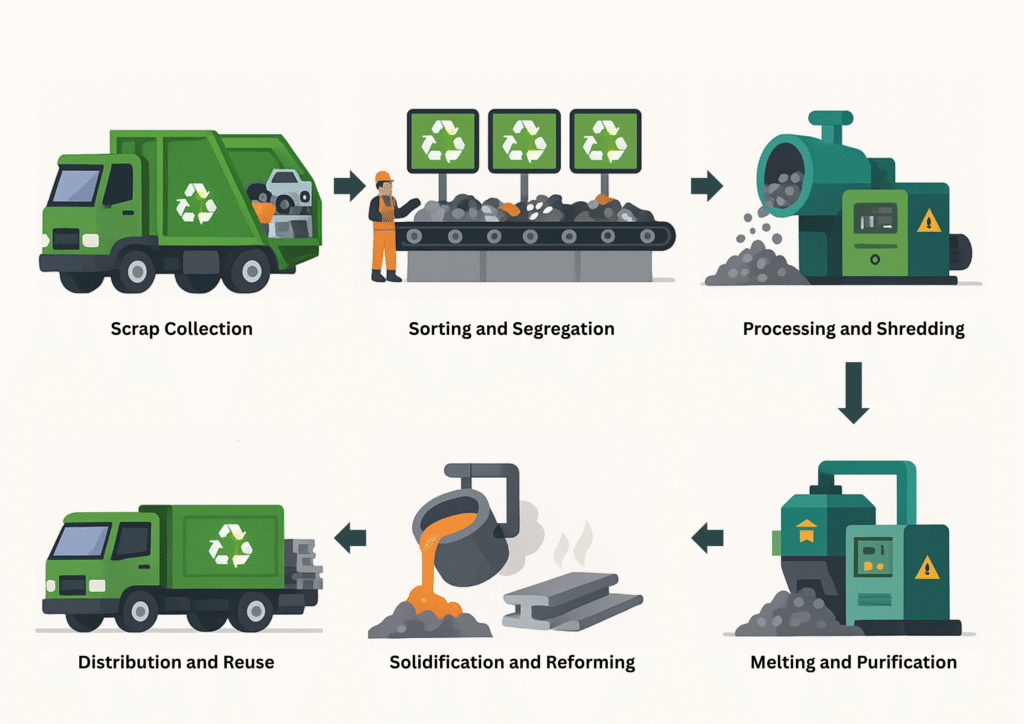
1. Scrap Collection
The journey commences with scrap collection, which is the first and most important stage.
Scrap materials originate from various sources, such as:
- Industrial units and construction sites
- Old vehicles, machinery, and appliances
- Households and offices
- Demolition or renovation projects
At A Sai Scrap, we make sure of timely pick-up and collection through eco-friendly transport. Our team categorizes materials like iron, copper, aluminium, brass, paper, and plastic right at the collection site for better efficiency.
2. Sorting and Segregation
Collected scrap materials of all types are transported to a sorting facility.
Here, they are distinguished based on:
- Material type: metal, plastic, paper, etc.
- Magnetic properties (ferrous vs. non-ferrous metals)
- Recyclability and contamination level
Advanced machinery consists of magnets, shredders, and eddy current separators that help sort out the material in an efficient manner. Proper segregation ensures that only pure and recyclable materials reach the next stage.
3. Processing and Shredding
After sorting, the scrap is processed and shredded into smaller, manageable pieces.
This step serves to:
- Reducing transportation costs
- Increasing the surface area for melting
- Ensuring uniform recycling
For instance, heavy-duty shredders cut metal scrap into small pieces. These smaller pieces are easy to handle and can melt efficiently at the recycling plants.
4. Melting and Purification
Next, the shredded materials are sent to recycling plants where they are melted in furnaces at high temperatures. Each type of metal-iron, copper, aluminium, and so on-is melted separately to keep the metals pure. After melting, other methods like electrolysis or filtration purify the material to get quality material.
5. Solidification and Reforming
Once purified, the molten material is poured into molds or cooled to form:
- Metal sheets
- Ingots
- Rods or blocks
These can then be reused by a number of different industries to manufacture new products, machinery, or construction materials — completing the recycling loop.
6. Distribution and Reuse
Finally, the refined materials are transported to the manufacturing and production units, where they are transformed into new products.
In such a process, wastes are granted a new life that helps industries reduce their dependence on virgin raw material, thus promoting a cleaner and greener environment.
Why This Process Matters
Every stage of the scrap recycling process contributes to:
Reducing landfill waste
Saving energy and natural resources
Lowering greenhouse gas emissions
Supporting sustainable industrial growth
At A Sai Scrap, we take pride in managing this entire process efficiently and responsibly — from scrap collection to final recycling — ensuring both environmental and economic benefits.